- Make sure Microsoft PowerPoint is up-to-date
- Make sure that Adobe Acrobat Pro is up-to-date
- Download PAC 2024 (external website)
An example file, Powerpoint-Example.pptx (PPTX 7MB), has been created which has issues that need to be corrected.
Title, Author etc.
While Title is the only field that is required, it is worth adding Tags for SEO, Subject, and right click on Author(s)’s name to “Remove Person” if you do not wish their name all over the internet – replace Author with organisation name.
Headings
Use the Title and Sub-Title placeholders because Microsoft PowerPoint does not have headings like Microsoft Word
In a new blank presentation, there will be these two options on a new page
Master slides
The slide content should be outlined in the headings, which helps AT users comprehend the page layout and navigate to interesting content:
- Master Layout title = Heading 1
- Layout Master title = Heading 2
Check if there is a parent slide called Slide Master by selecting View menu and choosing
The slides below the Slide Master are the Layout Master

On the Slide Master there are Title and Footers checkboxes
If the presentation does not have Master and Layout slides, right click on the main slide, select Layout and select Title Slide
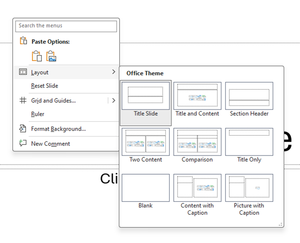
If the slide contains text that seems to be Title text but is not within the Title Section
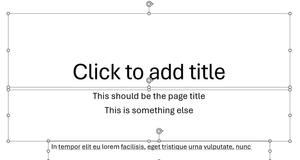
Move that text into the Title section using Cut and Paste

Making sure there is a Title element for each slide
Often elements do not have a proper Title in the reading order and might be given something such as “Rectangle1” or “TextBox1". Labelling the title textbox correctly as a Title attribute within the Selection Pane enables the AT to understand the hierarchy of the information on the slide better
Open Selection Pane on the Home tab, click on “Select” and choose Selection Pane
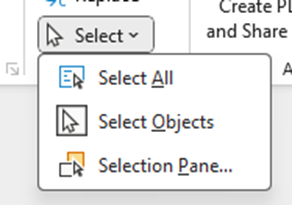
The Selection Pane displays the objects on the slide and the order they are in currently – note: the order of the objects goes from the bottom to the top
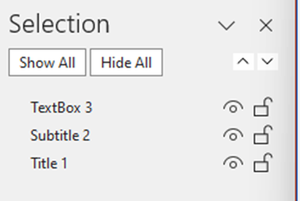
The objects can have their order changed by dragging and dropping into the right order
The order can also be controlled using the
“Check Accessibility” in the Review menu and selecting the
– note: the Reading Order pane goes from the top to the bottom
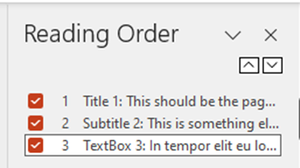
Lists
Use the inbuilt document list controls within Microsoft PowerPoint to add ordered lists (numbers) and unordered lists (bullet points)
AT users can understand lists created as lists because of the way content is organised
Lists will communicate helpful information such as:
- How many items the list has
- Where the list starts and where the list finishes
- Which list item the user is on
Hyperlinks
- The destination of links should be communicated accurately and clearly
- Use URL shortening services such as Bitly (external website) or TinyURL (external website) if the document is to be printed, if not, make sure the link text is meaningful (link shorteners can be viewed as a security risk as the destination cannot be seen unless the link has been clicked!)
- Screen readers will generally provide a list of links so make sure the link text is meaningful
- Do not use “click here” or “more information” for all the link text because it will not be possible to distinguish the links from each other
Alternative text for images (alt text)
- Alt text is used to convey the content of the image to those who can’t see it
- Screen readers will declare the image, then read the alt text
- Images that have no informative content and are purely decorative do not require alt text, but may require markup so that Assistive Technology understands that they should be ignored
- Remember to avoid punctuation as it is voiced
- MakeThingsAccessible has a guide to creating meaningful alternative text
Image use
- Only use images that support the text of the document
- Try avoiding the use of an image instead of text
- Make sure images have alt text unless they are decorative
Language
Leading screen reader software is multilingual.
Language of document
The language of the document must be set so that screen readers will read the document using the correct language profile.
Language of part of document
Content within the document written in a different language to the document’s default language must be identified.
Tables
- Do not use tables to control layout
- Use tables to communicate relationships between data
- Make sure headers are identified
- Try to keep the table simple
- If the table is complicated, can it be split into multiple tables or into lists?
Plain English
- Make sure sentences are short and concise, around 20-25 words
- Make sure words are kept simple
- Use common words. Complicated longer words (8 or 9 letters) will cause readers to skip shorter words (3,4, or 5 letters) that follow
- Use an Active voice rather than a Passive voice
- Where possible, use words containing one to two syllables
- Aim the language used at the level of a 9 year old as recommended by GOV.UK (external website) – remember in the UK, 7.1 million adults read at, or below, the level of an average 9 year old. WCAG 3.15 Reading Level (AAA) (external website) recommends providing a simplified version of the text if it requires a reading age of more than 12 years old
- Use contractions, words made up of two short words joined with an apostrophe such as I’ve, can’t etc.
- Do not use double negatives
- Explain the unusual, to help give full information
Why use it?
- The use of Plain English helps all users, including those who’s English is not their main language, and those who have cognitive impairment
- If the content is easy to read, it will be easy to understand when converted into alternative formats such as braille, or being read aloud by a screen reader
- Clear content converts more easily into British Sign Language
Further help
- Free services, guides, and resources to help are available from the Plain English Campaign (external website)
- Measure the readability of the text using Hemingway Editor (external website)
Font
- Use a font that is “sans-serif” and clear such as Arial, Helvetica, or Verdana
- Minimum font-size of 12
- For continuous text, avoid using capitals - letters in lowercase are read more easily
- Do not use underlining and italics because they could make text harder to read
- Bold and large font can be helpful when emphasising and highlighting text
- Make sure that text is justified to the left, as this helps to make sure there is an even gap between words, and enables the start and end of each line to be found easily
Colour
- Do NOT use colour by itself to show meaning
- Make sure that there is adequate contrast between background and text – use TPGi’s Colour Contrast Analyzer (CCA) (external website) to check contrast
Accessibility Checker (external website) tests Microsoft PowerPoint documents for accessibility issues and gives errors, warnings, tips, and intelligent services.
Errors
- All non-text content has alternative text (alt text)
- Tables specify column header information
- All sections have meaningful names
- Slide titles are unique
- Document access is not restricted
Warnings
- Table has a simple structure
- Sufficient contrast between text and background
- Closed captions are included for inserted audio and video
- Reading order of the objects on a slide presentation is logical
Tips
- Section names are unique
- Slide titles are unique
Intelligent Services
Suggested alternative text.
Review menu -> Check Accessibility -> Check Accessibility
The Errors reported are:
- Missing Object Description (24)
- Missing Table Header (2)
- Missing Slide Title (1)
- Default Section Name (2)
The Warnings reported are:
- Missing Audio or Video Subtitles (1)
- Hard-to-Read Text Contrast (3)
- Use of Merged or Split Cells (2)
- Check Reading Order (5)
The Tips reported are:
- Duplicate Slide Title (3)
- Duplicate Section Name (1)
The Intelligent Services reported are:
- Review Auto-Generated Description (2)
Language
Note:
- A PDF created by PowerPoint may not have any heading structure, caused by document authors not using headings in the original document
- PowerPoint creates a
<Sect>tag for each slide of the document when it created the PDF, and they may be many<Sect>tags containing other tags such as<P>on each slide.
Language of document
Go to File menu and select Options (which is at the bottom)
Select the Language
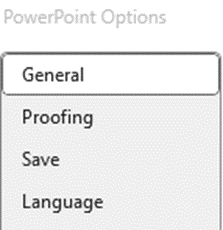
Select the default language required, then

Language of part of document
- Select text that is of a different language to the main document
- Review menu -> Language -> Set Proofing Language -> language required
Title
The Accessibility Checker does not test for the title in PowerPoint so this needs to be done manually.
To add the Title, File menu -> Info and click into the Title in the Properties section

Copy the contents of the Title into the Subject field
Add applicable SEO keywords into Tags field
Delete Author and replace with generic author such as organisation name
Tables
Tips for accessible tables
- Include a title describing what the table is represents
- Include at least one header row
- Do not merge or split cells
- Do not leave blank columns or rows
- Include alternative text
- Do not create nested tables
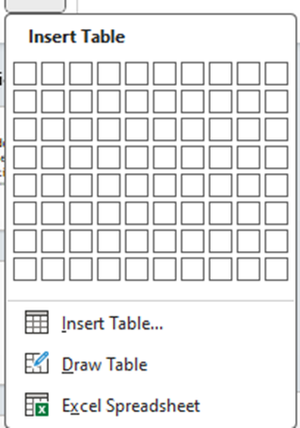
Inserting a table
Insert menu -> Table
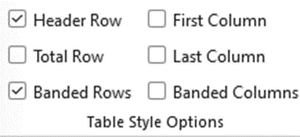
Make sure Header Row is selected in Table Design, and the First Column if the first column is also headings
Note: Scope must be fixed using Adobe Acrobat Pro.
Editing a table
- Select the table and make sure that Table Design menu is showing
- Select top row of cells and change Styles from “Table Contents” to “Table Heading”
Adding Alternative text to a table
Older versions of PowerPoint
Select the table needing alt-text and right-click, then select

In the Format Shape,

there is an Alt-Text option
PowerPoint 365
Select the table needing alt-text and when

is showing, right-click, then select
Lists
Bulleted lists (which can be images) and numbered lists are available
On Home tab, select the appropriate icon

Hyperlinks
Hyperlink text is the same as the link address

The link text is the full url
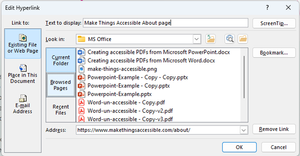
Right click and “Edit Link”
Change the Text to display field to be descriptive text
Text has now changed

Click on
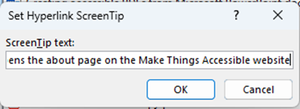
to add text that explains what clicking the link does
Note: Adobe Acrobat will automatically make text that appears to be a hyperlink clickable as a hyperlink without it being a proper hyperlink in the PDF document so text like below

will be clickable in the exported PDF and should be made into a hyperlink in the original document using good link text

Colour contrast
Use Colour Contrast Analyser (CCA) (external website) to test the text colour contrast manually and change any colours that fail.
Using colour for meaning
Do not use more than one colour when denoting the difference between specific content and the rest of the document

Amend the red text to black and make it bold

Errors
Missing Object Description
This error is because the object requires Alt-text.
Select down-arrow on object name
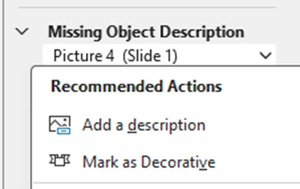
Either “Add a description” if the object requires alt-text or “Mark as Decorative” to artifact the image
Alternatively, right click on object and choose “View Alt Text…” to enter Alt-text or mark as decorative
Missing Table Header
This is because the table does not have a header row.
Select down-arrow on object name, then select “Insert Header Row” if there is not a row that should be the header
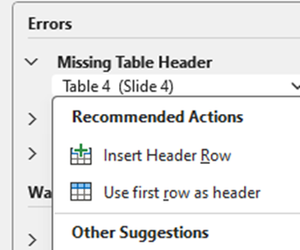
Or “Use first row as header” if there is
Missing Slide Title
This is because the slide has not had a title added.
Select down-arrow on object name, then select “Edit Slide Title”
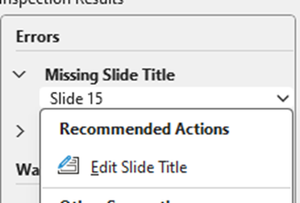
Click “Click to add title” and add title
Default Section Name
This is because a section has been added but not been renamed from the default.
Select down-arrow on object name, then select “Rename Section”
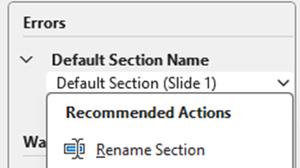
Change text within Section name
Warnings
Warnings are issues that may be fixed but do not necessarily need to be.
Missing Audio or Video Subtitles
This is because the embedded video does not have subtitles.
This cannot be fixed as it is an external third party video. Options include:
- contacting the owner of the video and asking if they will add subtitles
- creating a transcript of the video and adding the transcript immediately below the video, I used https://soundtype.ai/ (external website) downloaded to my mobile phone to do this
- removing the video from the presentation, if the two previous suggestions are not available
Hard-to-Read Text Contrast
This warning is because of the colour contrast between the text and the background
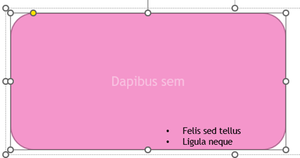
Select down-arrow on object name, then select “Change Colors”
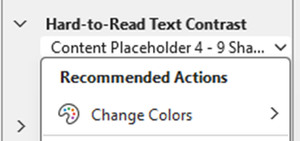
Select a colour that has enough of a colour contrast
To fix this, select the text and change the text colour

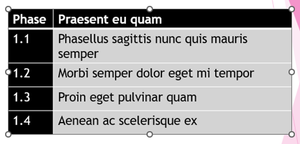
Use of Merged or Split Cells
This is because cells within the table are merged or split.
The options are to remove these cells from the table by simplifying the table, in this case the table

Was split into two separate tables

But these simpler tables still have merged cells where the title is – potentially the numbering could be removed and included at the start of each sentence, or the heading split into two cells with a heading of chapter (or something similar)
Check Reading Order
Select down-arrow on object name, then select “Verify object order”
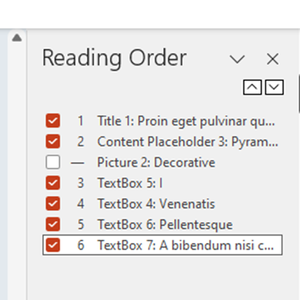
The Reading Order pane allows objects to be dragged into the correct reading order - Text box 4 and Textbox 5 were in the incorrect places
Tips
Duplicate Slide Title
This is because there is more than one slide with the same title.
Select down-arrow on object name, then select “Edit Slide Title”
Make the title unique
Duplicate Section Name
This is because there is more than one section with the same title.
Select down-arrow on object name, then select “Rename Section”
Make the section name unique
Intelligent Services
Review Auto-Generated Description
Select down-arrow on object name, then select “Approve description”
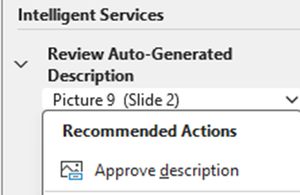
Verify description or mark as decorative, the first image is going to be marked as decorative, and and the second image is going to have the alt text verified. The Alt Text says:
“A close up of a logo
Description automatically generated”
As this is not acceptable, it has been set to "Make things accessible logo"
Auto-Generated Description turning on or off
Automatic Alt Text can be turned off or on by going to File menu and selecting Options (which is at the bottom)
Select

And checking or un-checking

Reading order
Open up the Reading Order pane by choosing the Accessibility tab and then selecting

Go through each slide and make sure that the reading order is correct
- File menu, Export, “Create Adobe PDF” or “Save as Adobe PDF” to use PDFMaker or go to the Acrobat tab (if Adobe Acrobat Pro is installed)
- Options and check that correct settings have been checked
- Or File menu, Save a Copy, change file type to PDF
- Click “More options…”, Options
- Make sure that to include “Document structure tags for accessibility”
Header and Footer objects are artifacted when exported to PDF.
- “Walk” the Tag Tree by clicking on the first item in the tree, then using the down arrow key (and right arrow key to open the tag where applicable, list etc.) so that the order the PDF is read can be checked
- In this case everything is good but if it is not, the tags will need to be rearranged into the correct order
- Click on “All tools” menu, “Prepare for accessibility” and choose “Check for accessibility” and “Start Checking”
- The document fails on “Tab order failed”, right click and “Fix” (hence order checked before doing this)
Errors in Accessibility Checker
Documents (3 issues)
- Logical Reading Order needs manual check
- Title – Failed
- Colour contrast – needs manual check
Tables (1 issue)
- Regularity – Failed
- Summary - Skipped
Errors in PAC 2024
Logical Structure
Structure Elements
Tables
Table header cell assignments
- Table header cell has no associated subcells –2 errors
Table regularity
- Irregular table row – 4 warnings
“Figure” structure elements – 2 warnings
Alternative Descriptions
- Alternative description for annotations – 1 error
Metadata and Settings
Metadate
- PDF/UA identifier – 1 error
Document settings
- Display of document title in window title – 1 error
Documents
Logical Reader Order
“Walk” down the Tag tree to check that the reading order is as expected and fix if it is not.
Title
This failed because even though the document had a Title, Author and Keywords, the “Initial View” was set to Show “File Name” rather than “Document Title”, clicking Fix sorted that out.
Color contrast
Go through the document with Colour Contrast Analyser (CCA) (external website) to make sure all the contrasts are still ok.
Tables
Regularity
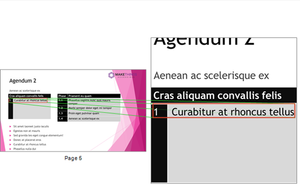
A regularity failure is because the table does not have the same number of cells in each row or in each column. In this case because there are only two columns of headers, but two columns inside each header column.

To fix this a span will need to be added to the “Cras aliquam convallis felis” cell and to the “Phasellus sagittis nunc quis mauris” cell so that each cell covers two columns.
The “1” cell and “Curabitur at rhoncus tellus” cells will need to have spans added covering four rows.
Prepare for accessibility menu
Fix Reading order
Click into table
Click on “Table Editor”
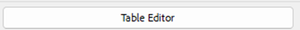
Select cell, right-click, “Table Cell Properties”
Set the cell to the correct type “Header Cell” if it’s a header, “Data Cell” if it is not
Sets correct spans
The table should look like this once complete

Summary
Table summaries used to be required to describe the table, the number of columns and rows etc. for AT so that it can announce this information. It is no longer necessary and the

and the fact it was skipped is not a failure and it could be ignored.
If nothing has been done on the table at all
- Select All tools > Prepare for accessibility > Fix Reading order
- Select the table by drawing a rectangle around it
- In the Reading order dialog box, select Table
- Right-click (Windows) or Ctrl-click (Mac OS) Table
- Click Edit Table Summary
- Enter a summary and select OK
If the table has already been modified to correct issues
- Select All tools > Prepare for accessibility > Fix Reading order
- Select the table by drawing a rectangle around it
- Right-click (Windows) or Ctrl-click (Mac OS) Table
- Click Edit Table Summary
- Enter a summary and select OK
Errors in PAC 2024 after fixing issues in Accessibility Checker
Logical Structure
Structure Elements
Tables
Table header cell assignments
- Table header cell has no associated subcells –1 error
Alternative Descriptions
- Alternative description for annotations – 1 error
Metadata and Settings
Metadate
- PDF/UA identifier – 1 error
Table header cell has no associated subcells
- Prepare for accessibility, Fix reading order
- Select table, Table Editor
- Right click in cell and “Table Cell Properties”
- The second cell had picked up the span from the heading cell so the span needed removing
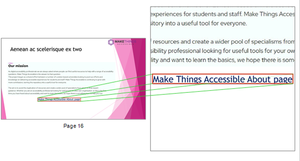
Alternative description for annotations
In the Link Properties, the “Select Action” was “Execute a menu item”
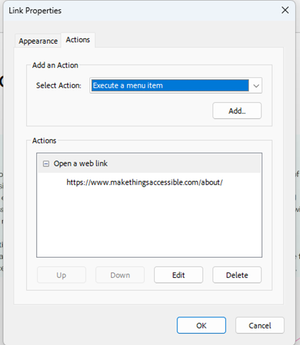
This was amended to “Open a web link”, then search for Pre in the “Find text or tools” search box
Choose
and click on

Under “Interactive elements and properties”
Select

and then click on
Save new version of document
PDF/UA identifier
This should only be added when the document passes everything else.
Search for Pre in the “Find text or tools” search box
In “Document info and Metadata” select

and click Fix button
Save new version of document
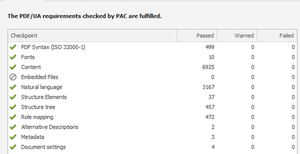
The document has now fully passed PAC 2024.
Creating accessible PDFs from Microsoft Powerpoint (Word 2.09MB)
- Accessible Document Basics
- How to handle blank data cells in accessible tables (external website)
- Accessibility Checker and Accessibility Check
- Rules for the Accessibility Checker (external website)
- Improve accessibility with the Accessibility Checker (external website)
- TPGi’s Colour Contrast Analyzer (external website)
- Writing for GOV.UK (external website)
- Plain English Campaign (external website)
- Hemingway Editor (external website)
- WebFX Readability Test (external website)
- Plain English – Advisory eLaHub (external website)
- WCAG 3.15 Reading Level (AAA) (external website)
- Creating meaningful alternative text
- Everything you need to know to write effective alt text (external website)
- PAC 2024 (external website)
- Table Accessibility in Word and PowerPoint (external website)
- Getting accessible templates for Office (external website)
- PowerPoint document accessibility (external website)
